2022 Research Highlights from Kavli Institutes
Remarkable basic research in astrophysics, theoretical physics, nanoscience, and neuroscience

At the 20 Kavli Institutes around the world, scientists explore the boundaries of our knowledge in astrophysics, theoretical physics, nanoscience, and neuroscience. As 2022 draws to a close, we share research highlights from these institutes to illustrate the remarkable basic research happening within these fields.
The highlights below are but a small sampling of the work done at the Kavli Institutes, where hundreds of researchers work tirelessly to expand our knowledge in these exciting and dynamic fields. We invite you to explore our monthly research highlights, and delve deeper into the science by visiting the institutes' websites.

Astrophysics
- The Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) revealed a dynamically evolving environment around a repeating fast radio burst source.
- Researchers marked the successful startup of the LUX-ZEPLIN dark matter detector at the Sanford Underground Research Facility.
- The PUEO (Payload for Ultrahigh Energy Observations) received the go-ahead from NASA to soar over Antarctic ice in search of signals from high-energy neutrinos.
- Researchers used gamma rays to detect a small neighboring galaxy filled with dark matter.
- Early findings from the Hydrogen Epoch of Reionization Array (HERA) telescope promise deeper understanding of the cosmic dawn.
- Astronomers developed a novel way to ‘see’ the first stars through the fog of the early universe.
Nanoscience
- Scientists discovered one-way superconductivity without magnetic fields, something that was long thought to be impossible.
- Researchers discovered a mechanism that ‘splits’ electron spins in magnetic material.
- Scientists described "topological dissipation," a fundamentally new concept to topological physics.
- An experimental method known as randomized compiling can dramatically reduce error rates in quantum algorithms and lead to more accurate and stable quantum computations.
- Researchers captured a rhodopsin receptor signaling cascade across a native membrane.
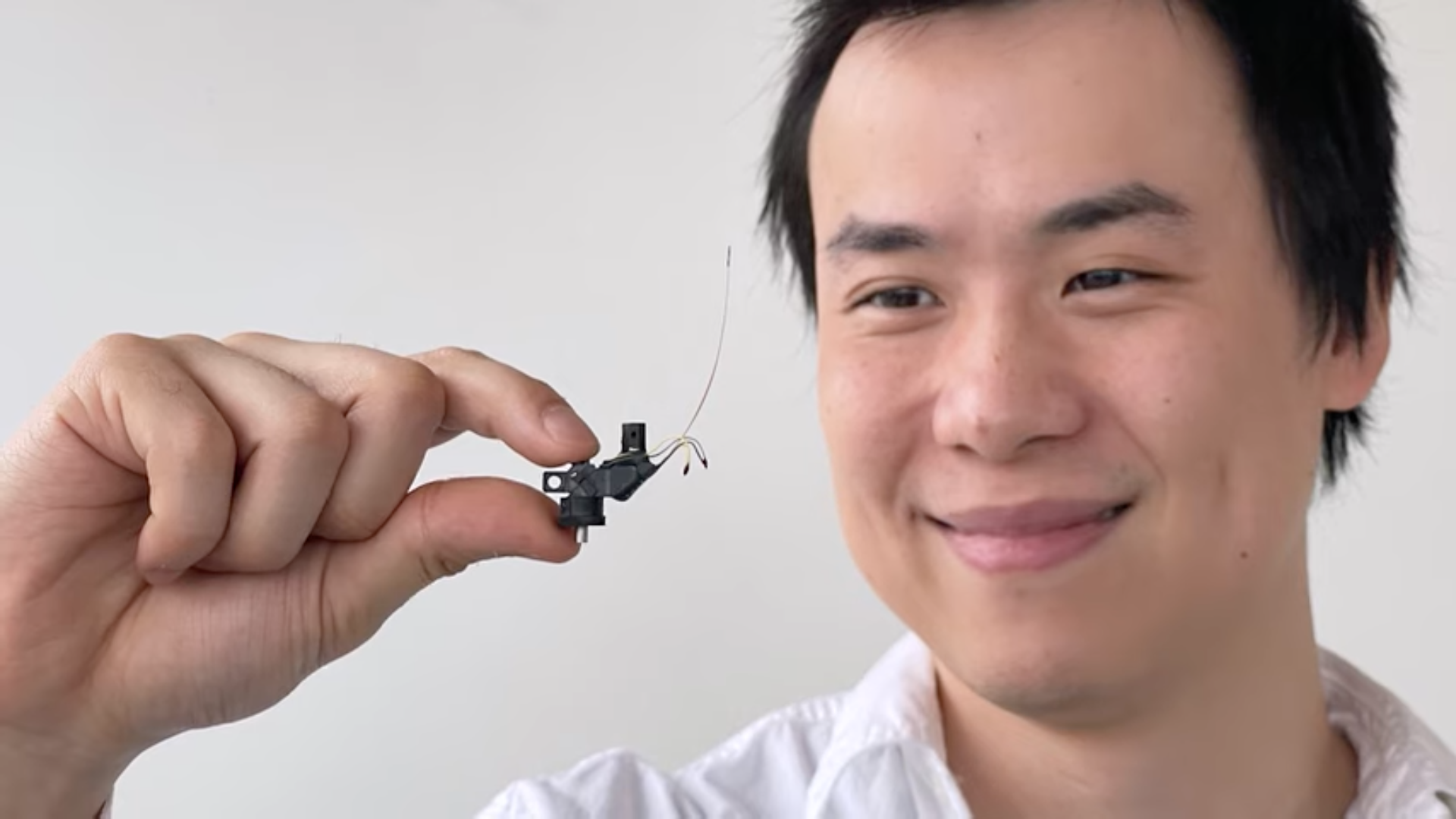
Neuroscience
- Fate mapping of neural stem cell niches reveals distinct origins of human cortical astrocytes.
- The development of a miniature 2-photon miniscope for large-scale calcium imaging in freely moving mice allows stable simultaneous recording of more than a thousand cells across multiple planes of densely active cortical regions.
- Scientists created a system to track millions of connections among brain cells in mice, all at the same time, providing an unprecedented view of brain cell activity in a synapse.
- The Telomere-to-Telomere (T2T) Consortium presented the complete 3.055 billion–base pair sequence of a human genome.
- Scientists provided new insight into the function of a protein called VPS13C, one of the molecular suspects underlying Parkinson’s.
- Scientists developed a new technique to study the dynamic interaction of place cells during navigation.
- A study showed how astrocytes may contribute to neurodevelopmental disorders.