Neutrino Discovery: A Step Closer to Finding CP Violation
(Originally published by the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU))
June 5, 2017
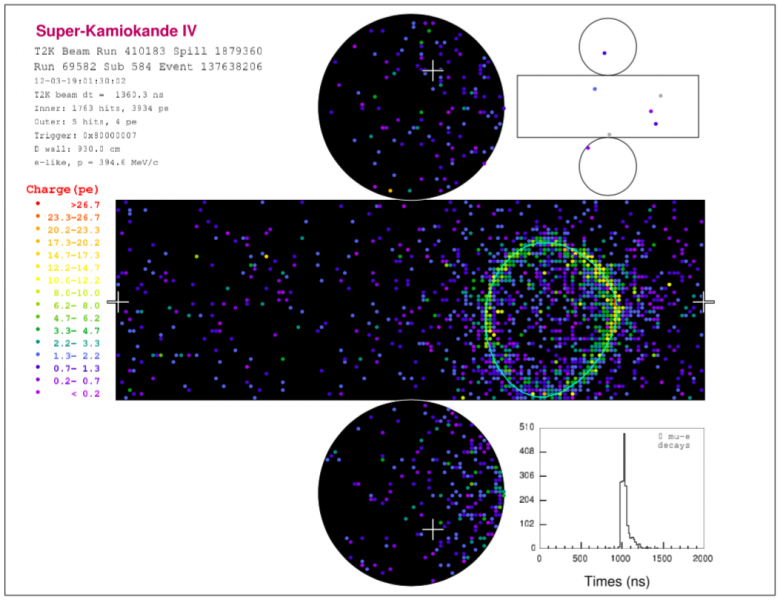
The different rates of neutrino and anti-neutrino oscillations recorded by an international collaboration of researchers in Japan--including from the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe--is an important step in the search for a new source of asymmetry in the laws that govern matter and antimatter.
The Standard Model of particle physics describes the basic building blocks of matter and how they interact. It also makes a point that for every particle created, there is an anti-particle. However, the Standard Model does not explain why our Universe still exists today, since the matter and anti-matter symmetry implies that matter--including galaxies, stars, and even humans--should have been annihilated by the equal amounts of anti-matter.
This violation of symmetry, called the charge-parity (CP) violation, has been observed experimentally, but not enough to explain the large amount of matter existing in the Universe.
The international T2K (Tokai-to-Kamioka) collaboration is the first experiment in the world that can search for CP violation by studying neutrino and anti-neutrino oscillations. High intensity beams of muon neutrinos (or muon anti-neutrinos) are produced at J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) on Japan’s east coast, and fired towards the Super-Kamiokande detector 295 km away in Gifu Prefecture. On the way, the neutrinos and anti-neutrinos spontaneously change 'flavor' from muon neutrinos or anti-neutrinos, to electron neutrinos or anti-neutrinos. A difference in the rates of oscillations in separate neutrino and anti-neutrino beams would be proof of an imbalance between particles and anti-particles, and that there is new physics to be learned beyond the Standard Model.
The first data set by T2K was published in April, and detected 32 electron neutrinos and 4 electron anti-neutrinos.
"While the data sets are still too small to make a conclusive statement, we have seen a weak preference for large CP violation and we are excited to continue to collect data and make a more sensitive search for CP violation,” said T2K collaborator and Kavli IPMU Project Assistant Professor Mark Hartz.
Recently, the T2K experiment has finished collecting another set of data that has doubled the amount of data available in the electron neutrino configuration, and its results are expected to be presented later this year. Hartz has said they expect to continue to take data for another 10 years.
"If we are lucky and the CP violation effect is large, we may expect 3 sigma evidence, or about 99.7% confidence level, for CP violation by 2026," he said.
Details of T2K's most recent results using neutrino and anti-neutrino data were published in Physical Review Letters as an Editors Suggestion on April 10.